What are KPIs?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are specific metrics used to evaluate the performance of companies, departments, processes, or projects in relation to their strategic goals. They are key factors that reflect success or failure in particular areas, serving as a basis for management decisions. Unlike general metrics, KPIs are carefully selected indicators directly aligned with the most critical success factors of a company. KPIs can include both financial and non-financial aspects, depending on the goals being pursued. For example, customer satisfaction could be a KPI in a service company, while production costs per unit might serve as a KPI in a manufacturing firm. By focusing on such relevant indicators, KPIs enable targeted and efficient management of business performance.
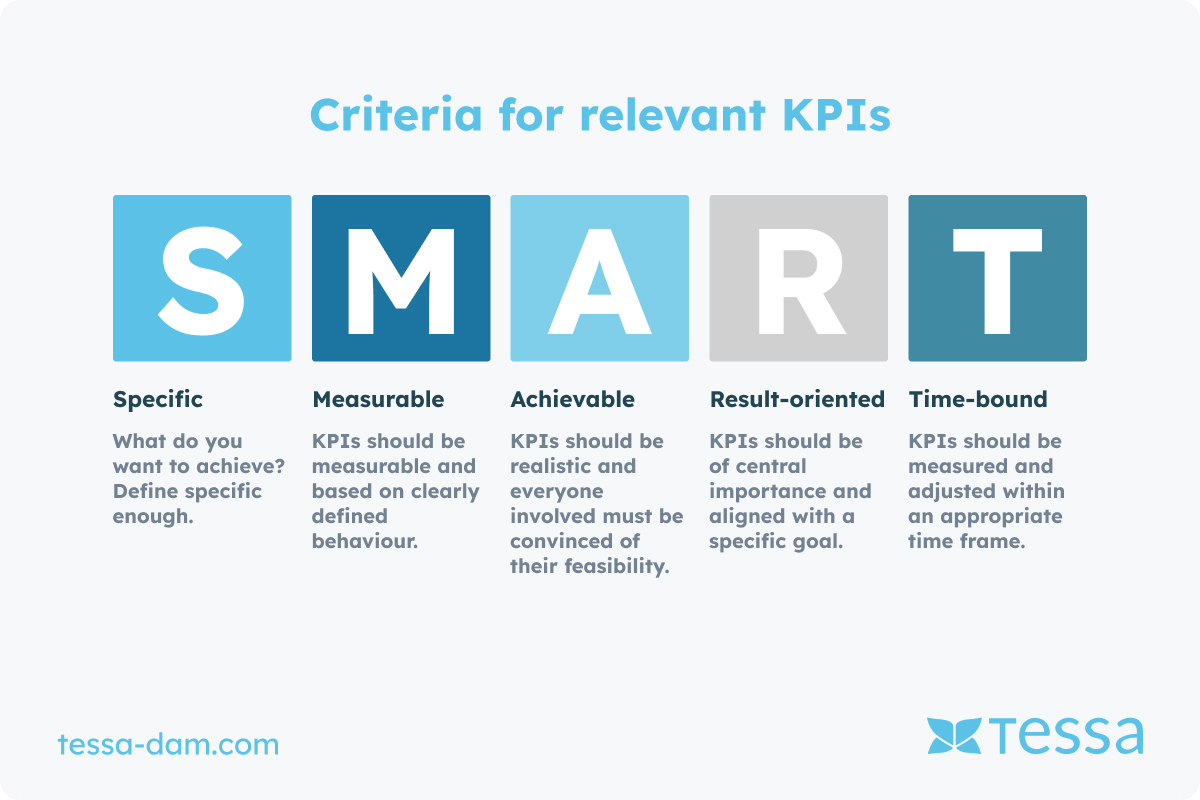
KPIs should meet specific criteria to ensure the data and information collected are useful. The SMART formula can help define appropriate and relevant KPIs.
How are KPIs calculated?
Calculating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) begins with clearly defining the goals to be measured and identifying relevant data sources. A KPI is typically calculated using a specific formula that translates these data into a measurable metric. This process can involve both simple and complex calculations, depending on the type of KPI and the underlying data.
A fundamental step in calculating a KPI is selecting the right metrics that directly relate to the company’s strategic goals. For instance, calculating a financial KPI like profit margin might involve dividing net profit by total revenue. For a non-financial KPI, such as employee satisfaction, survey results could be converted into a scale and represented as an average score.
Beyond simple calculation, benchmarking plays a crucial role: KPIs should be contextualized by comparing them to internal or external standards. This allows performance to be viewed not just in isolation but in relation to best practices or competitors. KPI calculation is an ongoing process that must be regularly reviewed and adjusted to align with changing business goals and market conditions.
What is the difference between metrics and KPIs?
Metrics are general measures used in business management to monitor and analyze various aspects of company performance. They provide a quantitative basis for evaluating processes, resources, and outcomes. In contrast to KPIs, which focus on a company’s key success factors, metrics cover a broad range of operational activities and are often more tactical in nature.
For example, total revenue is a metric that measures the total sales value over a given period. Other examples include production volume, the number of new customers, or employee turnover rates. These metrics provide valuable information but do not directly indicate the achievement of strategic goals. They are primarily used to monitor day-to-day operations and help identify and correct deviations early.
While metrics and KPIs are closely related, they differ in function and application. Metrics measure a broad spectrum of business activities, while KPIs focus on the critical success factors directly linked to the company’s strategic objectives. Therefore, KPIs tend to be more specific and targeted than general metrics.
Another key difference lies in their usage: KPIs are often utilized at the management level to make strategic decisions and ensure the long-term success of the company. In contrast, metrics are mainly used at the operational level to manage and optimize daily operations. For example, while total revenue might be an important metric, the KPI could be the profit margin, which directly measures financial success and operational efficiency.
Developing and implementing strategic KPIs
Developing and implementing strategic KPIs requires a systematic and focused approach, beginning with the clear definition of the company’s strategy. The first step involves precisely formulating the company’s long-term goals, from which specific KPIs can be derived to measure the success of these goals. It is crucial that KPIs directly reflect the company’s strategic priorities and cover relevant success factors.
Another critical aspect is the selection of appropriate metrics and data sources. These metrics should be reliably and consistently available to ensure accurate and continuous monitoring of the KPIs. This often requires close collaboration between various departments to ensure that the necessary data are collected and analyzed.
Once the KPIs are established, the next step is to integrate these indicators into existing management processes. This includes regularly reviewing and reporting on the KPIs to ensure they are driving the desired outcomes. It is also important to implement a feedback system that allows KPIs to be adjusted or further developed as business goals or market conditions change.
Finally, communicating the strategic KPIs within the company is of great importance. Employees at all levels need to understand how their work contributes to achieving strategic goals and how KPIs measure this progress. Clear communication and training can help align the entire organization towards a common direction and promote effective strategy implementation.
Challenges and success factors in using strategic KPIs
The use of strategic KPIs comes with several challenges that must be addressed to ensure their effectiveness. One of the biggest challenges is selecting the right KPIs that are truly meaningful for the company’s long-term goals. There is often a risk of defining too many or too few KPIs, which can lead to either data overload or insufficient guidance.
Another issue can be data quality. Strategic KPIs require accurate and reliable data, but in practice, there can be gaps or inconsistencies in the available information. This not only complicates accurate measurement but can also lead to misinterpretations that negatively impact strategic decisions.
Furthermore, strategic KPIs need to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market or within the company. Static KPIs that are not adjusted to changing circumstances quickly lose their relevance and can cause the company to adhere to outdated goals.
The success factors in using strategic KPIs lie in the continuous review and adjustment of the indicators, as well as in involving the entire organization in the process. Regular monitoring and proactive adjustments to KPIs are essential to maintain their relevance. Additionally, employee training and awareness play a key role in ensuring that KPIs are not only embedded at the management level but also in day-to-day operations.
Another success factor is integrating KPIs into the company culture. When the importance of KPIs and their goals is understood and accepted by all employees, the likelihood of effectively achieving strategic objectives increases. Ultimately, the success of strategic KPIs depends on how well they are integrated into overall strategic management and how consistently they are incorporated into decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Strategic KPIs for sustainable success
Strategic KPIs are critical metrics that evaluate a company’s progress toward its long-term goals, requiring careful selection, reliable data, and flexible adaptation. Their successful implementation depends on clear integration into business processes and broad employee involvement. Through continuous review and integration into company culture, they significantly contribute to strategic management and long-term competitiveness.